| Company: Amazon |
| Founded on: July 5, 1994 |
| Headquarters: Seattle, Washington, and Arlington, Virginia, USA |
| CEO: Andrew Jassy |
| Number of Employees (2025): 1,556,000 (Full-time and Part-time) |
| Type: Public Company |
| Ticker: AMZN |
| Market Cap (April 2025): $2.18 Trillion |
| Consolidated Annual Revenue (FY 2024): $637.96 Billion |
| Consolidated Net Revenue (FY 2024): $59.25 Billion |
| Net Margins (FY 2024): 9.29% |
When was the last time you placed an online order? It was probably from Amazon. Amazon is now the place to go for almost anything, whether it’s groceries, a blender, or a book. But how did a small online bookstore turn into one of the most powerful companies in the world?
Amazon is more than just a massive online retailer these days. It’s changing how we communicate with our gadgets, stream, store data, and even shop. Amazon is present everywhere, from lightning-fast deliveries to cloud services that run some of the largest companies in the world.
However, there is more to the story behind all of that innovation and convenience. What specifically contributes to Amazon’s success? Where is it still having trouble? And what dangers might it encounter soon?
In this Amazon SWOT Analysis, we’ll learn the strengths that drive its growth, the weaknesses that could hinder its growth, the opportunities it’s yet to explore, and the challenges it needs to watch out for.
SWOT Analysis of Amazon
Strengths | Amazon SWOT Analysis
Strong Brand Value
In 2025, Amazon ranked 4th in the Global Brand Rank by Brand Finance, with a brand value of $356.4 billion, up 15.36% from last year.
This showcases the company’s worth in the global market.
Customer Centric Approach
Amazon always comes to mind when we think about companies that focus on their customers. Since they started 1-click ordering in 1999 and let customers post reviews, including the bad ones, they’ve worked hard to improve the shopping experience.
The launch of Prime showed just how much they care about saving customers’ time and keeping them loyal. These steps have built Amazon’s image as a customer-first business, making it a reliable choice without unnecessary spending.
Wide Range of Offerings
Amazon delivers a wide range of products and services across multiple sectors, making it a dominant player in both digital and physical markets.
Through the Amazon Store, it offers millions of products from global third-party sellers, while AWS leads in digital infrastructure.
Plus, Amazon has its hands in AI, entertainment with services like Prime Video and Twitch, smart gadgets like the Alexa, Echo, and Kindle, and a strong network for quick deliveries everywhere.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is not only a global leader in cloud computing but also Amazon’s most profitable business unit. In 2024, AWS generated $107.56 billion in revenue and delivered $39.83 billion in operating income, which translates to a strong operating margin of 37.04%.
To put this in perspective, AWS’s operating income accounted for approximately 67.23% of Amazon’s total net income of $59.25 billion, highlighting its critical role in the company’s financial performance.
This level of profitability gives Amazon the flexibility to reinvest heavily in R&D, pursue global expansion, and drive innovation across its ecosystem.
Best in People Management
Amazon has an incredible reputation as a top employer in addition to being a customer-obsessed company. In April 2025, LinkedIn released a report titled ‘Best Employers in the US,’ in which Amazon secured the 2nd rank.
This ranking sounds reasonable considering the company’s significant hourly wage raise and additional benefits for its hourly U.S. employees, including paid time off and better health care options.
With its Upskilling 2025 pledge, Amazon offers career opportunities to its employees in industries that will grow in the future.
These efforts show Amazon’s dual commitment to enhancing employee well-being and preparing its workforce for the future, strengthening its reputation as both a consumer-first and people-first company.
Third Party Sellers
More than 60% of revenue in the Amazon store comes from Third-party sellers. It enables Amazon to diversify its revenue channels, such as seller fees, fulfillment services, and advertising.
Moreover, a wide range of global independent sellers results in greater product variety and competitive pricing, enhancing customer retention and helping Amazon solidify its presence as a global brand.
Amazon also enjoys massive data from this ecosystem, through which it leverages to identify trending products, consumer purchasing psychology, and pricing strategies. Using these insights, Amazon develops and sells its products under several private labels, which helps the company earn higher margins.
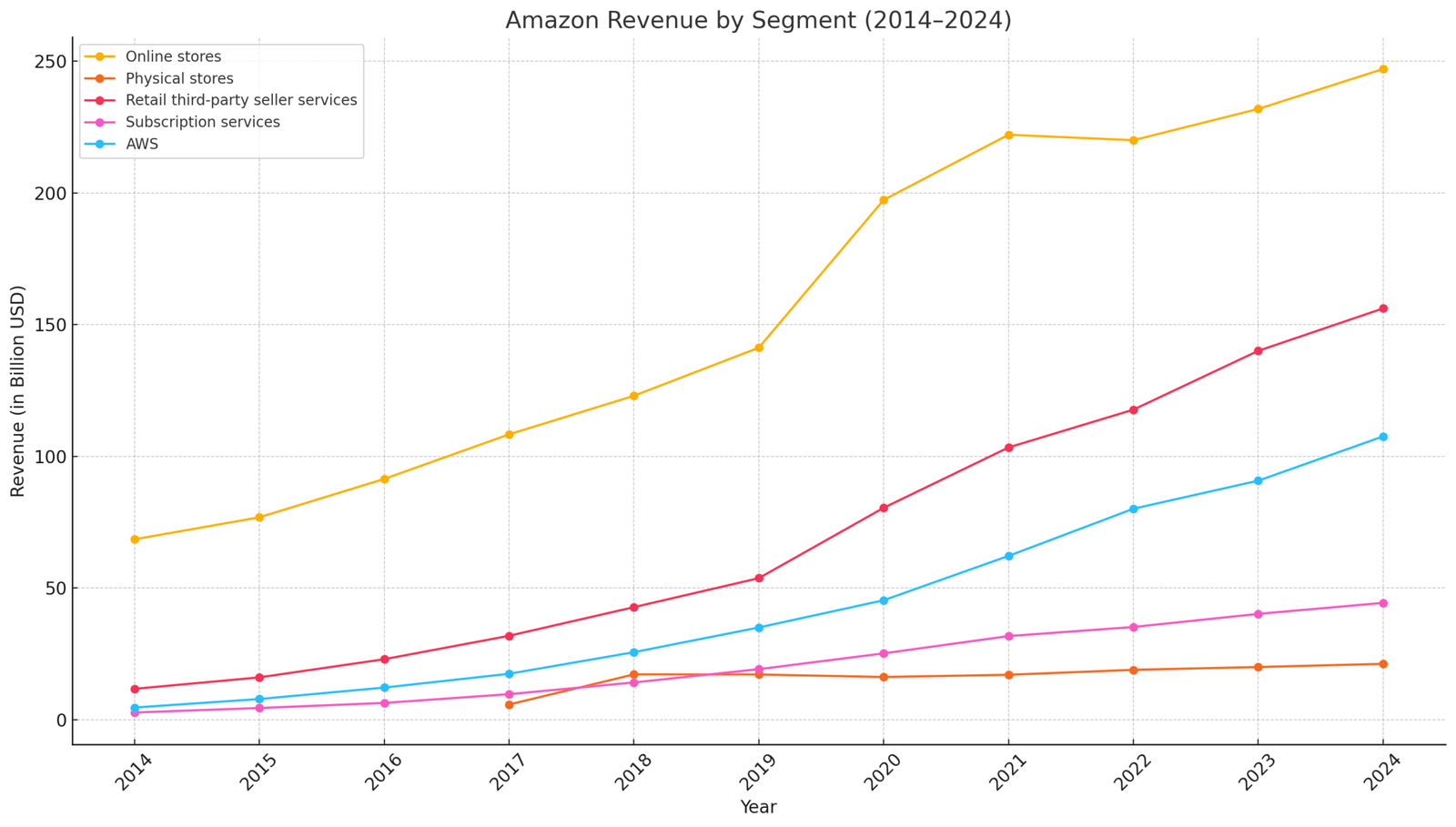
Steady Revenue Growth
Amazon is reporting growth in revenue across all its segments of operations over the years, whether we look at revenue from its AWS in 2024, which grew to $107.56 billion, an 18.5% jump from the previous year.
Revenue from physical stores also grew by approximately 6% in 2024, highlighting the company’s efforts to scale in the offline market too. From online stores, it generated a revenue of $247.03 billion, growing by around 6.5%.
As we saw in the last point, Amazon is home to around 60% third-party sellers, from which the company made a revenue of $156.15 billion, a 11.5% growth in 2024. From Subscription services, revenue reached $44.37 billion, grew by 10.37% compared to 2023.
This steady growth journey of Amazon translates its operational efficiency across the product group, making it one of the strongest companies in the world.
Actions Towards Sustainability
Amazon has been using 100% renewable energy for electricity across its global operations since 2023, seven years ahead of its 2030 target, reflecting its commitment to sustainability. This clean energy supports its growing infrastructure, including data centers and fulfillment networks.
Amazon has deployed over 24,000 custom electric delivery vans and aims to expand this fleet to 100,000 by 2030. In 2024, it delivered more than 1 billion packages across the US.
In addition to energy and transportation efforts, AWS is working to become water positive by 2030, returning billions of liters of water to communities through conservation and replenishment projects.
Beyond its operations, Amazon supports suppliers through the Sustainability Exchange and promotes environmentally responsible shopping through its Climate Pledge Friendly label. It also co-leads The Climate Pledge, targeting net-zero carbon emissions by 2040.
Weaknesses | Amazon SWOT Analysis
Limited Offline Stores
As of 2025, Amazon is in the brick-and-mortar space with around 623 stores, including 543 Whole Foods Market (acquired in 2017), 63 of Amazon Fresh, and 17 of Amazon Go. Over 95% of these stores are in the US.
Amazon also launched Amazon Books, Amazon 4-Star, and Pop-Up stores, but due to underperformance, it had to close them down in 2022.
Despite its vast global reach online, Amazon’s limited global offline footprint and closures in the physical retail formats highlight a strategic weakness in capturing the full omnichannel retail experience.
DEI Policy
In late 2024, Amazon announced it to scale back its Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) efforts, which reflects a potential weakness in its internal strategy and corporate values.
The company’s decision to phase out multiple DEI programs and merge employee groups neutralizes its years of advocacy for inclusive initiatives. It also raises concerns about its long-term commitment to workplace inclusion.
Overdependence on AWS
As we discussed earlier, AWS is the backbone of Amazon’s profitability. Relying heavily on AWS can be concerning.
It might show double-digit growth QoQ and YoY, but over the last three straight quarters, it didn’t match the expected growth rate, because of rising competitors’ market share in the cloud infrastructure market.
Product Liability
Amazon relies largely on third-party sellers, which limits its control over product quality and safety. This has sometimes led to dangerous items being sold, like faulty carbon monoxide detectors and flammable clothes for kids.
The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) voted unanimously to consider Amazon a ‘distributor’ under the Consumer Product Safety Act, which means Amazon can be held responsible for recalls and safety fixes.
This translates to a product liability for Amazon to monitor product safety, address hazards in advance, and maintain customer trust, especially as regulations get stricter.
Union Protests
In December 2024, just before Christmas Eve, Amazon faced its largest-ever labor strike in the U.S., involving 10,000 workers led by the Teamsters.
Such unrest during a peak sales period raises concerns about Amazon’s employee relations and potential revenue loss during high-demand times.
Opportunities | Amazon SWOT Analysis
Personal Shopper Experience
Amazon has a solid opportunity to grow in the personalized fashion market with its Personal Shopper service.
As more people seek convenience and tailored shopping experiences, this service can help Amazon attract new customers, increase its average order value, explore new fashion categories, and expand its market share.
Additionally, insights gathered from shopper preferences can enhance recommendation algorithms, and Amazon can use this data to boost its private label sales, making it a smart and scalable path for future growth.
Expansion into International Markets
Amazon’s major revenue comes from the US. The vast international market is still not tapped to its full potential. The growth rate Amazon can enjoy in international/emerging markets can’t be seen in the US anymore.
According to Statista, the Retail E-commerce sales in the US will grow by 9.06% from 2025 to 2029 annually (CAGR). This is lower than the worldwide average of 9.6%.
Right now, the company has viable resources to expand internationally, to safeguard the future of its stakeholders.
Attitude of Innovation and Adaptation
Amazon has a strong track record in terms of innovation and learning what the market needs.
Despite being discontinued, the Fire Phone, Amazon Wallet, and Test Drive laid the foundation for significant achievements. The Fire Phone’s AI efforts contributed to the creation of Alexa, Wallet evolved into Amazon Pay, and Test Drive played a role in strengthening AWS’s infrastructure.
These experiences provide Amazon with the opportunity to continue exploring new markets and technologies, transforming bold experiments into potential industry-leading solutions.

Strategic Acquisitions
Amazon has acquired more than 100 companies to date. Some notable acquisitions across various industries were IMDb, Audible, Kiva Systems, Twitch, Whole Foods, Ring, Zoox, and MGM Studios.
It also joined the race to acquire TikTok with a last-minute bid. If the deal goes through, it could become a major win for Amazon in the long run, offering advantages across several strategic areas.
These acquisitions give Amazon valuable opportunities to diversify its revenue streams, boost its technological capabilities, and expand or strengthen its position in new and existing markets.
Leveraging its Omnichannel Capabilities
According to Deloitte, retailers are focusing on creating seamless omnichannel experiences to meet the changing expectations of consumers.
Amazon can leverage this by enhancing the integration of online and physical retail channels, like Whole Foods and Amazon Go stores, to offer a cohesive shopping experience.
This approach combines the convenience of e-commerce with the immediacy of shopping in-store.
Quick Commerce
Amazon has a huge opportunity to double down on quick commerce in major markets. By expanding micro-fulfillment centers (dark stores) in key urban areas, Amazon can meet the growing demand for ultra-fast delivery.
It can optimize routes and inventory management by utilizing its existing logistics network and AI tools, which can further lower costs and boost efficiency.
With ‘Tez‘, Amazon has entered India’s quick-commerce market, showcasing its dedication to quick global expansion in this field.
Threats | Amazon SWOT Analysis
Competition
The company is facing intense competition in the US and the global market.
Walmart is the biggest rival in the physical retail experience and E-commerce. Alibaba, eBay are taking the pie in the online shopping space. Netflix, Apple TV+, and Disney+ are rivaling in the subscription race. Microsoft Azure and the Google Cloud Platform market share are increasing in the cloud infrastructure services market.
Otto, eBay; Bunnings, eBay; Alibaba, JD.com, and Pinduoduo are rivaling Amazon in the European, Australian, and Chinese markets, respectively.
Flipkart, founded in 2007 in India and now owned by Walmart, currently holds a larger market share than Amazon.
Despite Amazon’s success, fierce global rivals constantly pressure its growth, innovation, and market share.
Trade War
To mitigate the trade deficit, the Trump-led administration imposed tariffs on several countries with which the US trades. Many nations, including China and the European Union, are criticizing this move and threatening to impose retaliatory tariffs on the US.
This can impact Amazon’s sellers and the company as a whole, as tariffs will make the sourcing of the products more expensive.
The inflated costs are likely to reflect on the consumer globally, which can make Amazon a less attractive place to buy online.
Removal of De Minimis
The Trump administration ruled to close down the De Minimis exemption. It translates to the end of duty-free treatment of imports valued under $800.
It’ll affect Amazon adversely, as the company just launched ‘Amazon Haul‘ in November 2024, to compete with low-priced platforms. Now, the loophole has been removed, which will no longer benefit Shein, Temu, and Amazon’s Haul.
Understand the impact of the De Minimis Exemption on the US fashion factory, Forever 21.
Overdependence on the US
Amazon heavily relies on the US market. In 2024, the company made a consolidated revenue of $637.96 billion, out of which around $438.02 billion came from the US itself.
Such overdependence on a single country may hamper the company’s balance sheet if the economy hits recession.
Packages Theft
Over 55% of the 1.7 million daily stolen packages in the U.S. are linked to their deliveries. Nearly 52% of Americans report losing an Amazon package, leading to frequent replacements or refunds.
Theft spikes during events like Prime Day, damaging customer trust and pushing Amazon to invest in secure delivery options, driving up operational costs, and complicating last-mile logistics.
Antitrust Lawsuit
Amazon is facing regulatory scrutiny in both the U.S. and abroad. The 2023 antitrust lawsuit filed by the FTC and 17 state attorneys general poses a serious threat to Amazon’s core business model.
If the FTC proves that Amazon abused its monopoly power to block competition and control prices unfairly, the company could face big fines or be forced to change how it operates.
It might also face restrictions on bundling services like Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) with better visibility on its marketplace.
Such legal outcomes could severely disrupt Amazon’s seller ecosystem, reduce its market dominance, and open the door for competitors to gain ground in the e-commerce landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Prioritizing customer experience is essential; it builds loyalty and forms a strong competitive advantage.
- Amazon’s scale brings unmatched strength but also increased regulatory and public scrutiny.
- Technology leadership requires ethical responsibility, especially concerning labor practices and data privacy.
- Continuous listening and adaptation to challenges are crucial for sustaining long-term success and leadership.
I hope you find this Amazon’s SWOT Analysis helpful. If so, please consider reading our other articles.
Share this article on your socials.

Sveiki, aš norėjau sužinoti jūsų kainą.
Sveiki, George, šiuo metu nesiūlome jokių kursų ar mokamų paslaugų.
This article really deserves to get viral bro! I’m bookmarking this SWOT Analysis for future updates.
Can you write one on Nike?
Thank you buddy for sharing this in-depth analysis!
Thanks Jack! Such comments really drive me to research and write such in-depth analysis.
Nike’s annual report is likely to be published by the last week of this month. So, you can expect the SWOT Analysis of Nike within the first week of July.
Keep reading…